Delving into DNA the Double Helix Coloring Worksheet Answer Key Biology Corner, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence. This comprehensive resource unveils the intricacies of DNA structure, replication, transcription, and translation, empowering learners to unravel the mysteries of molecular biology.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Introduction to DNA Structure

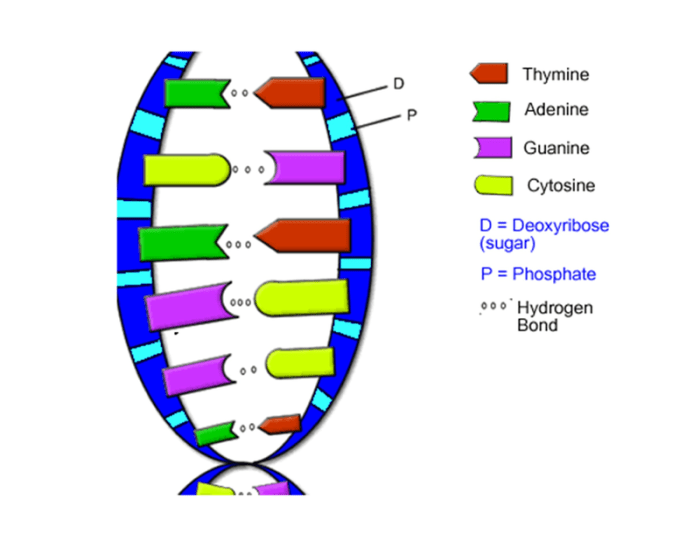
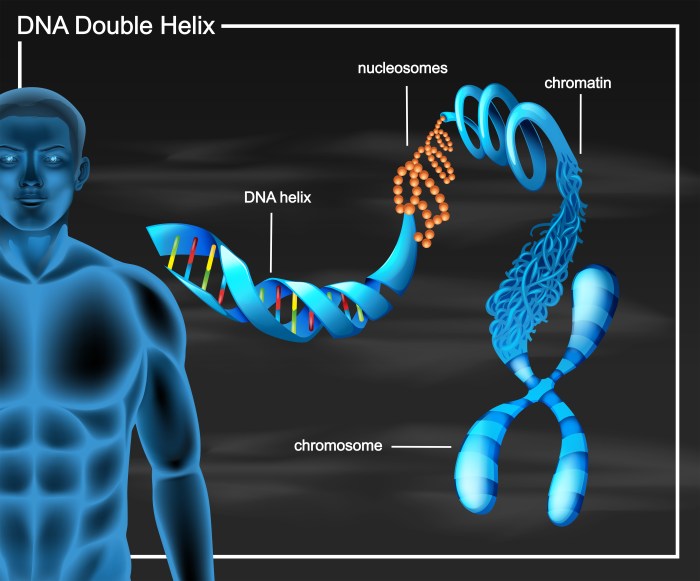
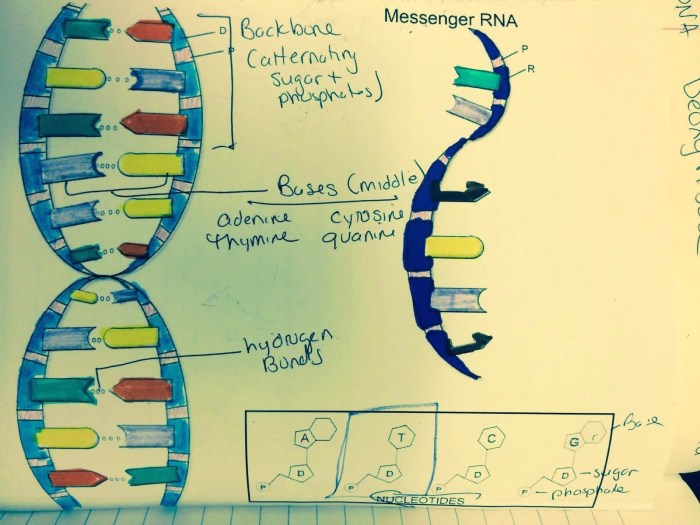
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries genetic information in living organisms. It is made up of two long strands that twist around each other to form a double helix shape. Each strand is composed of a series of nucleotides, which are the basic building blocks of DNA.
Nucleotides are made up of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other to form base pairs, which are the units of genetic information.
A always pairs with T, and C always pairs with G.
The double helix structure of DNA was first discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. This discovery was a major breakthrough in the field of biology, and it helped to pave the way for the development of modern genetics.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and growth. DNA replication begins when the double helix unwinds and the two strands separate. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
The new strands are synthesized by an enzyme called DNA polymerase, which adds nucleotides to the growing strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction. The end result of DNA replication is two identical double helices, each of which contains one original strand and one new strand.
DNA Transcription
DNA transcription is the process by which the information in DNA is used to make RNA. RNA is a molecule that is similar to DNA, but it is single-stranded and it contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). RNA is synthesized by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which binds to the DNA template and adds nucleotides to the growing RNA strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
The end result of DNA transcription is an RNA molecule that is complementary to the DNA template.
DNA Translation
DNA translation is the process by which the information in RNA is used to make proteins. Proteins are molecules that are essential for the structure and function of cells. DNA translation begins when an RNA molecule binds to a ribosome.
The ribosome then moves along the RNA molecule, reading the sequence of codons. Each codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for a specific amino acid. The ribosome adds amino acids to the growing protein chain in the order specified by the codons.
The end result of DNA translation is a protein molecule that is complementary to the RNA template.
Mutations and Genetic Disorders
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental factors, such as radiation, and genetic factors, such as errors in DNA replication. Mutations can have a variety of effects, depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation in the DNA sequence.
Some mutations are harmful, while others are neutral or even beneficial.
Genetic disorders are diseases that are caused by mutations in genes. Genetic disorders can be inherited from parents or they can occur spontaneously. There are many different types of genetic disorders, and the symptoms of genetic disorders can vary widely.
Some genetic disorders are mild, while others are severe or even fatal.
DNA Technology, Dna the double helix coloring worksheet answer key biology corner
DNA technology is a set of techniques that are used to study and manipulate DNA. DNA technology has a wide range of applications, including:
- Medicine:DNA technology can be used to diagnose and treat genetic disorders. For example, DNA technology can be used to identify mutations that cause genetic disorders, and it can be used to develop new treatments for genetic disorders.
- Forensics:DNA technology can be used to identify criminals and to solve crimes. For example, DNA technology can be used to match DNA samples from crime scenes to DNA samples from suspects.
- Agriculture:DNA technology can be used to improve crops and livestock. For example, DNA technology can be used to develop crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, and it can be used to develop livestock that are more productive.
FAQ: Dna The Double Helix Coloring Worksheet Answer Key Biology Corner
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helix molecule composed of nucleotides, each consisting of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The two strands of the helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs: adenine (A) with thymine (T), and guanine (G) with cytosine (C).
How does DNA replicate?
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process in which each strand of the double helix serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. Enzymes such as DNA polymerase facilitate the addition of nucleotides to the growing strand, ensuring the faithful duplication of genetic information.
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA provides the instructions for protein synthesis through the processes of transcription and translation. During transcription, a complementary RNA molecule is synthesized using DNA as a template. This RNA molecule is then translated into a protein by ribosomes, which read the RNA sequence and assemble the corresponding amino acids.