Write the rate law for the following elementary reaction: an essential task in chemical kinetics, providing a quantitative description of the relationship between the rate of a reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. Understanding and writing rate laws are crucial for predicting reaction rates, designing experiments, and unraveling the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
This guide delves into the concept of elementary reactions, explores the components of a rate law expression, and Artikels the methods for determining the rate law. It also provides a comprehensive table of examples from various fields of chemistry, showcasing the practical applications of rate laws.
Understanding Elementary Reactions
Elementary reactions are the simplest chemical reactions that cannot be broken down into simpler steps. They involve the direct interaction of a small number of reactants to form products.
Elementary reactions have the following characteristics:
- They are unimolecular, bimolecular, or termolecular.
- They have a single transition state.
- Their rate laws can be derived from the stoichiometry of the reaction.
Rate Laws, Write the rate law for the following elementary reaction
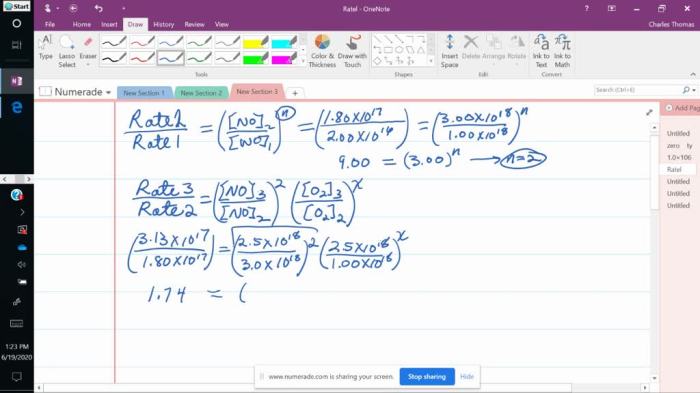
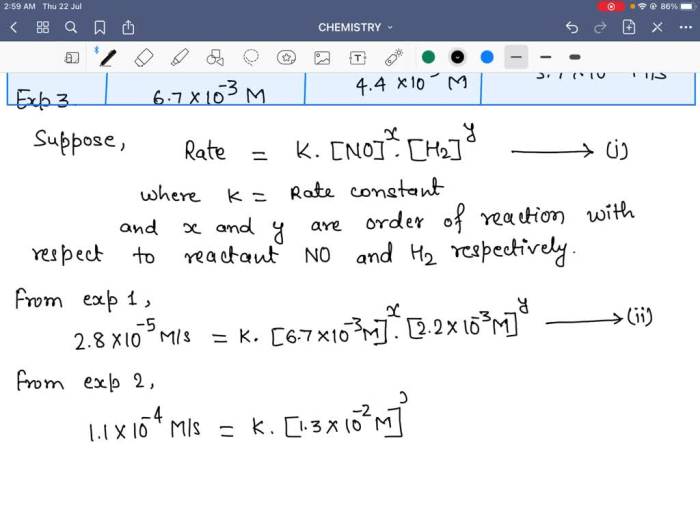
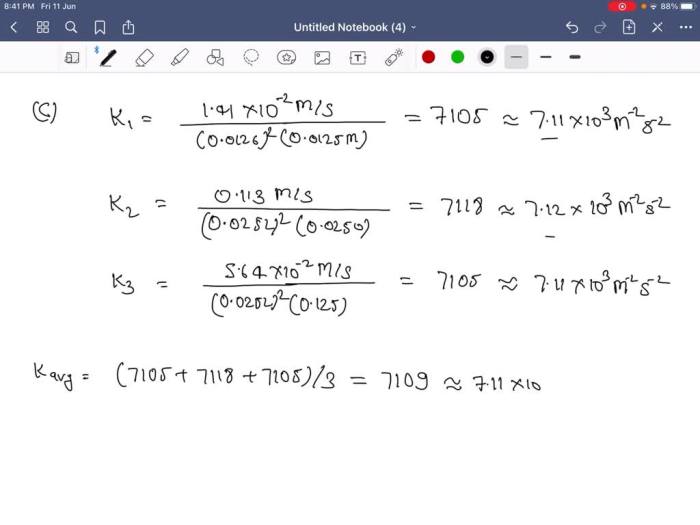
A rate law is an equation that expresses the relationship between the rate of a reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. The rate law for an elementary reaction is determined by the stoichiometry of the reaction and the rate constant.
Rate Law Expression
The rate law expression for an elementary reaction is written as:
Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n
where:
- Rate is the rate of the reaction.
- k is the rate constant.
- [A] and [B] are the concentrations of the reactants A and B.
- m and n are the orders of the reaction with respect to A and B.
The order of a reaction is the exponent to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law expression.
Determining the Rate Law
The rate law for an elementary reaction can be determined by:
- Measuring the initial concentrations of the reactants and products.
- Measuring the rate of the reaction at different concentrations of the reactants.
- Using differential and integral rate laws.
Differential rate laws express the rate of a reaction in terms of the instantaneous concentrations of the reactants. Integral rate laws express the rate of a reaction in terms of the change in concentration of the reactants or products over time.
Writing the Rate Law for an Elementary Reaction
The rate law for an elementary reaction can be written using the following general format:
Rate = k[A]^aA[B]^bB
where:
- k is the rate constant.
- [A] and [B] are the concentrations of the reactants A and B.
- aA and bB are the stoichiometric coefficients of A and B.
The units of the rate constant depend on the order of the reaction.
Examples of Rate Laws for Elementary Reactions: Write The Rate Law For The Following Elementary Reaction
| Reaction | Rate Law Expression | Rate Constant Units |
|---|---|---|
| A + B → C | Rate = k[A][B] | M^-1 s^-1 |
| 2A + B → C | Rate = k[A]^2[B] | M^-2 s^-1 |
| A + 2B → C | Rate = k[A][B]^2 | M^-1 s^-1 |
General Inquiries
What is the general format for writing the rate law for an elementary reaction?
Rate = k[A]^m[B]^n…
How do I determine the rate law for a reaction?
Conduct experiments to measure the reaction rate at different concentrations of reactants. Use differential or integral rate laws to analyze the data and determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant.
What is the significance of stoichiometric coefficients in the rate law?
Stoichiometric coefficients indicate the relative number of reactant molecules involved in the elementary reaction and determine the exponents in the rate law expression.