The maximum height at which a catenary scaffold can be erected is a critical factor in determining its safety and effectiveness. This comprehensive guide delves into the engineering principles, environmental influences, and industry applications that shape the maximum height of these versatile structures.
Catenary scaffolds, characterized by their distinctive parabolic shape, have revolutionized construction and maintenance projects by providing a stable and adaptable work platform at elevated heights. Understanding the factors that govern their maximum height is essential for ensuring their safe and efficient use.
1. Definition and Overview
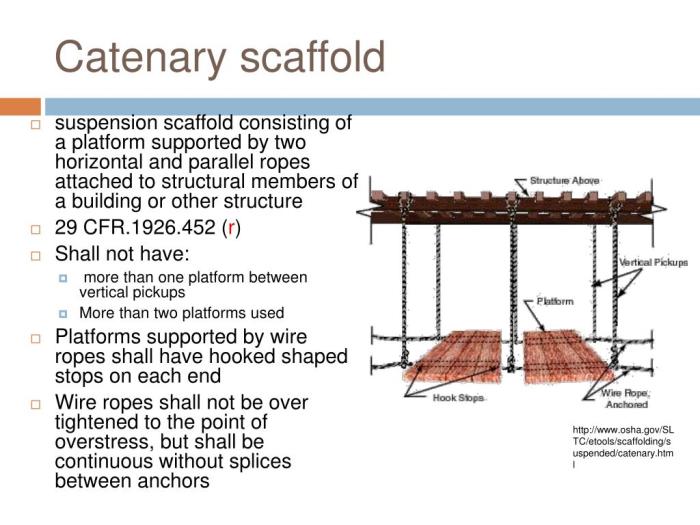
A catenary scaffold is a suspended scaffolding system that utilizes a cable or chain as its primary support structure. The cable is suspended between two fixed points, creating a curved shape that resembles an inverted catenary curve. This design provides inherent stability and load-bearing capacity.
Catenary scaffolds have a long history, dating back to ancient times when they were used for construction and repairs of tall structures. Today, they are widely employed in various industries, including construction, maintenance, and entertainment.
Types of Catenary Scaffolds
- Single-Span Catenary Scaffolds:Consists of a single cable suspended between two supports.
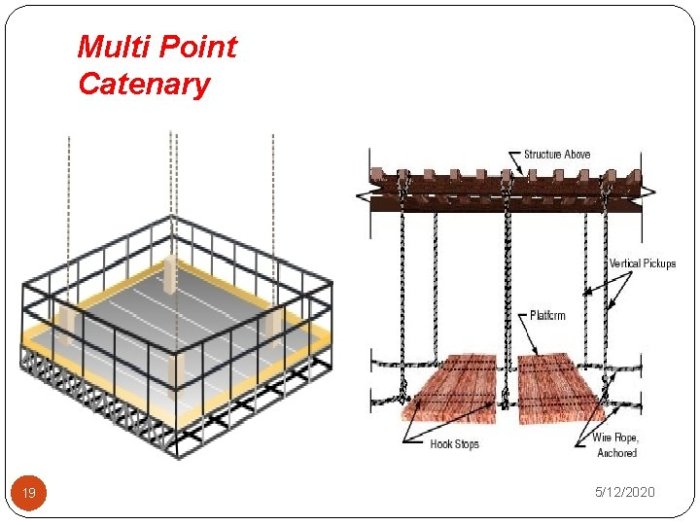
- Multi-Span Catenary Scaffolds:Employs multiple cables and supports to create a longer and more complex scaffold system.
- Truss-Supported Catenary Scaffolds:Incorporates trusses or beams to provide additional support and rigidity.
2. Factors Affecting Maximum Height

Scaffold Material, The maximum height at which a catenary scaffold
The material of the cable or chain used in the scaffold directly influences its maximum height. High-strength materials, such as steel or synthetic fibers, can withstand greater loads and allow for taller scaffolds.
Scaffold Design
The design of the scaffold, including the cable diameter, spacing, and support structure, plays a crucial role in determining its maximum height. A well-designed scaffold will distribute loads effectively and ensure stability.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as wind load, temperature fluctuations, and seismic activity, can impact the maximum height of a catenary scaffold. Adequate consideration of these factors is essential for ensuring the safety and integrity of the structure.
3. Calculations and Engineering Considerations
Calculating the maximum height of a catenary scaffold requires careful consideration of various engineering principles and formulas.
Formulas
The following formulas are commonly used to determine the maximum height:
H = (W/2T)- (L^2 – 4S^2) / 8S
Where:
H = Maximum height
W = Total weight of the scaffold and load
T = Tension in the cable
L = Length of the span
S = Sag of the cable
Engineering Principles
Engineering principles, such as the theory of elasticity, structural mechanics, and load analysis, are applied to ensure the safety and stability of the scaffold.
Safety Regulations and Standards
Various safety regulations and standards govern the design, construction, and use of catenary scaffolds. Adherence to these regulations is crucial for ensuring worker safety and preventing accidents.
4. Applications and Limitations: The Maximum Height At Which A Catenary Scaffold
Applications
Catenary scaffolds are commonly used in:
- Construction:For high-rise buildings, bridges, and other tall structures.
- Maintenance:For accessing and repairing facades, roofs, and other inaccessible areas.
- Entertainment:For erecting stages, rigging lights, and supporting sound systems.
Advantages
- Stability:The curved shape provides inherent stability, reducing the risk of collapse.
- Load-Bearing Capacity:Can support heavy loads and equipment.
- Versatility:Can be easily adapted to various shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages
- Cost:Can be more expensive than traditional scaffolding systems.
- Complexity:Requires specialized design and engineering expertise.
- Height Limitations:Maximum height is limited by factors such as material strength and environmental conditions.
5. Case Studies and Examples
Example 1: Burj Khalifa
The Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building, utilized a catenary scaffold system during its construction. The scaffold reached a maximum height of over 800 meters, providing access to workers and materials.
Example 2: Sydney Harbour Bridge
The Sydney Harbour Bridge underwent extensive maintenance in 2019 using a catenary scaffold system. The scaffold spanned over 500 meters and allowed workers to safely access and repair the bridge’s structure.
FAQ Explained
What is the typical maximum height of a catenary scaffold?
The maximum height of a catenary scaffold varies depending on factors such as material, design, and environmental conditions. However, it typically ranges from 30 to 100 feet.
How does the scaffold material affect its maximum height?
The strength and durability of the scaffold material play a significant role in determining its maximum height. Stronger materials, such as steel or aluminum, allow for higher scaffold heights compared to weaker materials like wood.
What environmental factors can influence the maximum height of a catenary scaffold?
Wind speed, temperature, and precipitation can all affect the stability of a catenary scaffold. High winds can sway the scaffold, while extreme temperatures can weaken the materials. Heavy rain or snow can add weight to the scaffold, reducing its load-bearing capacity.
