Bromination of e stilbene mechanism – The bromination of E-stilbene mechanism, a captivating journey into the realm of organic chemistry, unravels the intricacies of a fundamental reaction with far-reaching applications. This in-depth analysis unveils the step-by-step transformation, regio- and stereoselectivity, and influential factors that govern this intriguing process.
As we delve into the bromination mechanism of E-stilbene, we uncover the formation of the bromonium ion intermediate, a pivotal species that orchestrates the regio- and stereoselective addition of bromine to the double bond. The influence of temperature, solvent, and substituents on the reaction outcome further enriches our understanding of this versatile reaction.
Introduction
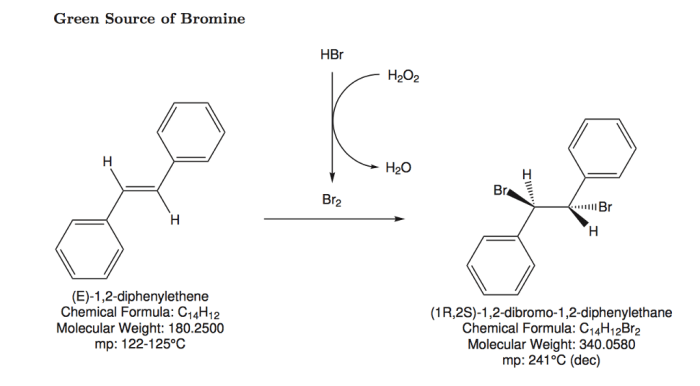
Bromination is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry, involving the addition of bromine atoms to unsaturated compounds. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various organic molecules, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and functional materials.
E-stilbene, a symmetrical alkene, is a widely studied compound in bromination reactions. Its well-defined structure and predictable reactivity make it an ideal model system for investigating the mechanism and selectivity of electrophilic addition reactions.
Analyzing the bromination mechanism of E-stilbene provides insights into the fundamental principles governing electrophilic aromatic substitution and helps predict the regio- and stereochemical outcomes of similar reactions.
Mechanism of Bromination
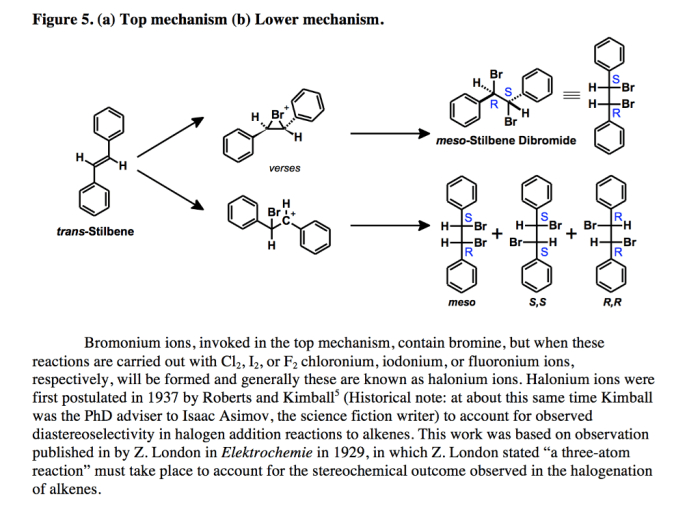
The bromination of E-stilbene proceeds via a two-step mechanism involving the formation of a bromonium ion intermediate.
- Electrophilic Addition:Bromine adds to the double bond of E-stilbene, forming a bromonium ion. The positive charge of the bromonium ion is stabilized by resonance, with the positive charge delocalized over the two carbon atoms of the double bond.
- Nucleophilic Attack:A bromide ion attacks the bromonium ion, opening the three-membered ring and forming the dibromide product. The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction are determined by the stability of the intermediate bromonium ion and the steric and electronic effects of the substituents on the stilbene ring.
Factors Affecting the Reaction
Several factors influence the rate and selectivity of the bromination reaction of E-stilbene:
- Temperature:Increasing the temperature increases the rate of the reaction but can also lead to side reactions, such as the formation of polybrominated products.
- Solvent:The polarity of the solvent can affect the stability of the bromonium ion and the rate of the reaction. Polar solvents, such as water, stabilize the bromonium ion and slow down the reaction, while nonpolar solvents, such as dichloromethane, favor the formation of the dibromide product.
- Substituents:Electron-donating substituents on the stilbene ring increase the electron density of the double bond, making it more reactive towards electrophilic addition. Electron-withdrawing substituents, on the other hand, decrease the reactivity of the double bond.
Applications of the Reaction: Bromination Of E Stilbene Mechanism
The bromination of E-stilbene has numerous applications in organic synthesis:
- Pharmaceuticals:Brominated stilbene derivatives are used as intermediates in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, including anti-cancer drugs and antibiotics.
- Dyes:Brominated stilbene derivatives are used as dyes and pigments in various industries, such as textiles, plastics, and printing.
- Functional Materials:Brominated stilbene derivatives are used as functional materials in optoelectronics, sensors, and other applications.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of the bromonium ion intermediate in the bromination of E-stilbene?
The bromonium ion intermediate plays a crucial role in the bromination of E-stilbene, facilitating the regio- and stereoselective addition of bromine to the double bond.
How does temperature influence the bromination reaction?
Temperature exerts a significant influence on the bromination reaction, with higher temperatures favoring the formation of the more stable trans-dibromide product.
What are the practical applications of the bromination of E-stilbene?
The bromination of E-stilbene finds applications in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other functional materials.