Ap statistics unit 4 test – Prepare to embark on an enthralling journey through AP Statistics Unit 4, where you’ll delve into the captivating world of data analysis and statistical inference. From hypothesis testing to regression analysis, this unit equips you with a comprehensive toolkit for making informed decisions based on data.
Throughout this exploration, we’ll uncover the significance of data analysis in statistics, examining various techniques employed in Unit 4. We’ll delve into the advantages and drawbacks of each method, empowering you to select the most appropriate approach for your statistical endeavors.
Data Analysis Techniques
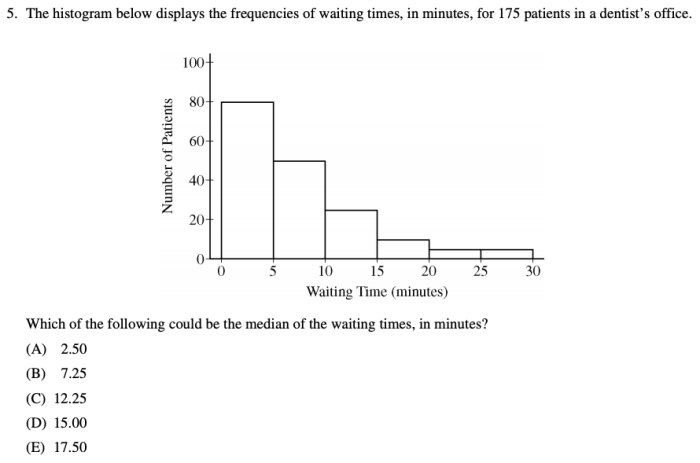
Data analysis is crucial in AP Statistics as it allows us to uncover meaningful patterns and insights from raw data. Unit 4 delves into various data analysis techniques, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics provide a concise summary of data. They include measures like:
- Mean: Average value of a dataset
- Median: Middle value when data is arranged in ascending order
- Standard deviation: Measure of data spread
Advantages: Easy to calculate and interpret; provides a quick overview of data.
Disadvantages: Can mask outliers; not as informative as inferential statistics.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics allow us to make inferences about a larger population based on a sample. They include techniques like:
- Hypothesis testing: Testing claims about population parameters
- Confidence intervals: Estimating population parameters with a margin of error
- Regression analysis: Modeling relationships between variables
Advantages: Provides insights beyond the sample; allows for generalization.
Disadvantages: Requires larger sample sizes; can be more complex to interpret.
Non-Parametric Tests
Non-parametric tests are used when the data does not meet certain assumptions, such as normality. They include techniques like:
- Chi-square test: Testing for independence between categorical variables
- Mann-Whitney U test: Comparing medians of two independent samples
Advantages: Do not require assumptions about data distribution; useful for small sample sizes.
Preparing for the AP Statistics Unit 4 test can be a daunting task, but remember that even amidst the challenging world of data analysis, there’s always a little room for a break. Take a quick detour to the whimsical world of Cathy the Queen of Cats , where you can chuckle at her feline antics.
After this refreshing interlude, return to your statistical endeavors with a renewed sense of focus and determination. Remember, even in the realm of numbers, a little bit of feline fun can go a long way.
Disadvantages: Less powerful than parametric tests when assumptions are met.
Hypothesis Testing
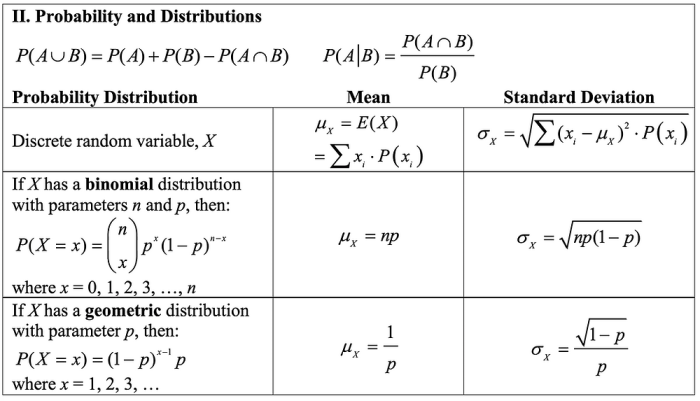
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether a particular hypothesis about a population is supported by the available evidence.
The steps involved in hypothesis testing are as follows:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Set the level of significance.
- Calculate the test statistic.
- Determine the p-value.
- Make a decision.
Examples of Hypothesis Tests Used in AP Statistics Unit 4
- One-sample t-test: This test is used to determine whether the mean of a population is equal to a specified value.
- Two-sample t-test: This test is used to determine whether the means of two populations are equal.
- Chi-square test: This test is used to determine whether the proportions of two or more categories are equal.
Statistical Inference

Statistical inference is the process of making an estimate or prediction about a population based on a sample. This is done by using the data from the sample to make an educated guess about the characteristics of the population as a whole.
There are two main types of statistical inference:
- Point estimation: This involves making an estimate of a single population parameter, such as the mean or proportion.
- Interval estimation: This involves making an estimate of a range of values within which the population parameter is likely to fall.
Statistical inference is used extensively in AP Statistics Unit 4. For example, it is used to:
- Estimate the population mean
- Estimate the population proportion
- Test hypotheses about population parameters
- Make predictions about future observations
Regression Analysis: Ap Statistics Unit 4 Test

Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It allows us to predict the value of the dependent variable based on the values of the independent variables.
Types of Regression Analysis
There are different types of regression analysis, each with its own purpose and assumptions:
Simple Linear Regression
Models the relationship between a single independent variable and a single dependent variable.
Multiple Linear Regression
Models the relationship between multiple independent variables and a single dependent variable.
Nonlinear Regression
Models relationships where the relationship between the variables is not linear.
Regression Analysis in AP Statistics Unit 4
Regression analysis is a key component of AP Statistics Unit
4. It is used to
- Predict the value of a dependent variable based on the values of independent variables.
- Test hypotheses about the relationship between variables.
- Create models to explain the relationship between variables.
Examples of regression analysis in AP Statistics Unit 4 include:
- Predicting the price of a house based on its square footage and number of bedrooms.
- Testing the hypothesis that there is a relationship between the amount of time spent studying and exam scores.
- Creating a model to explain the relationship between the age of a car and its resale value.
Chi-Square Tests
Chi-square tests are a type of statistical test used to determine whether there is a significant difference between the expected frequencies and the observed frequencies of a set of data. The chi-square statistic is calculated by summing the squared differences between the expected and observed frequencies, divided by the expected frequencies.
The resulting value is compared to a critical value from a chi-square distribution to determine whether the difference is statistically significant.
Types of Chi-Square Tests
There are several different types of chi-square tests, each with its own specific purpose:
- Goodness-of-fit test:Tests whether the observed frequencies of a set of data fit a specified expected distribution.
- Test of independence:Tests whether two categorical variables are independent of each other.
- Test of homogeneity:Tests whether two or more categorical variables have the same distribution.
Examples of Chi-Square Tests in AP Statistics Unit 4, Ap statistics unit 4 test
Chi-square tests are used in a variety of applications in AP Statistics Unit 4, including:
- Testing the goodness-of-fit of a normal distribution to a set of data.
- Testing the independence of two categorical variables, such as gender and political affiliation.
- Testing the homogeneity of two or more categorical variables, such as the distribution of blood types among different ethnic groups.
Nonparametric Tests
Nonparametric tests are statistical methods that do not require the assumption of a specific probability distribution for the population from which the sample was drawn. They are often used when the sample size is small, or when the data are not normally distributed.Nonparametric
tests are based on the ranks of the data, rather than on the actual values. This makes them less powerful than parametric tests, but also more robust to violations of the assumptions of normality and equal variance.
Types of Nonparametric Tests
There are many different types of nonparametric tests, each with its own purpose. Some of the most common nonparametric tests include:
- The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is used to compare the medians of two paired samples.
- The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare the medians of two independent samples.
- The Kruskal-Wallis test is used to compare the medians of three or more independent samples.
- The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient is used to measure the strength of the relationship between two variables.
Examples of Nonparametric Tests Used in AP Statistics Unit 4
Nonparametric tests are often used in AP Statistics Unit 4, particularly when the data are not normally distributed. Some examples of nonparametric tests that are used in AP Statistics Unit 4 include:
- The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is used to compare the medians of two paired samples, such as the scores of students on a pretest and a posttest.
- The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare the medians of two independent samples, such as the scores of students in two different classes.
- The Kruskal-Wallis test is used to compare the medians of three or more independent samples, such as the scores of students in three different schools.
- The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient is used to measure the strength of the relationship between two variables, such as the relationship between the number of hours students study and their scores on a test.
Nonparametric tests are a valuable tool for analyzing data that does not meet the assumptions of parametric tests. They are easy to use and interpret, and they can provide valuable information about the population from which the sample was drawn.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of data analysis in AP Statistics?
Data analysis is crucial in AP Statistics as it allows us to explore, interpret, and draw meaningful conclusions from data. It empowers us to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within data, enabling informed decision-making and problem-solving.
Can you provide examples of different data analysis techniques used in AP Statistics Unit 4?
Unit 4 covers a range of data analysis techniques, including descriptive statistics, graphical representations, probability distributions, and hypothesis testing. These techniques help us summarize, visualize, and make inferences about data.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using different data analysis techniques?
Each data analysis technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. Descriptive statistics provide a concise overview of data, while graphical representations help visualize patterns and trends. Probability distributions allow us to model the likelihood of events, and hypothesis testing enables us to draw conclusions about populations based on sample data.
The choice of technique depends on the specific research question and the nature of the data.